Health Informatics: IoT’s Next Frontier?
September 3, 2020 - 7 minutes read The Internet of Things (IoT) has improved many industries by connecting data and sensors to create systems that work in real-time to unearth insights about an organization’s productivity, operations, and equipment maintenance. Healthcare can benefit from IoT applications tremendously. With devices like wearables and analytical software, providers can find more value in vital informatics.
The Internet of Things (IoT) has improved many industries by connecting data and sensors to create systems that work in real-time to unearth insights about an organization’s productivity, operations, and equipment maintenance. Healthcare can benefit from IoT applications tremendously. With devices like wearables and analytical software, providers can find more value in vital informatics.
Data is the new standard of value in tech, and digital technologies like medical applications provide key information that drives decision-makers to make better choices for patients. During the COVID-19 pandemic, these innovations are needed more than ever before as patients stay away from doctor’s offices and hospitals to protect themselves from exposure to the virus.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis and treatment go hand-in-hand to help a patient recover from an illness or disease. In medicine, diagnosis based on symptoms and tests hinges on data analysis of a large group of people. Without a correlating case, symptoms and test results can look “abnormal”, especially for specialists who haven’t seen a case similar to the patient’s chart.
In pharmaceuticals, medicines can’t even reach the general public until strictly-controlled experiments are done on a substantial amount of patients. This early data informs whether the drug is safe, what patients it would work best for, and in what other scenarios we could apply the drug towards.

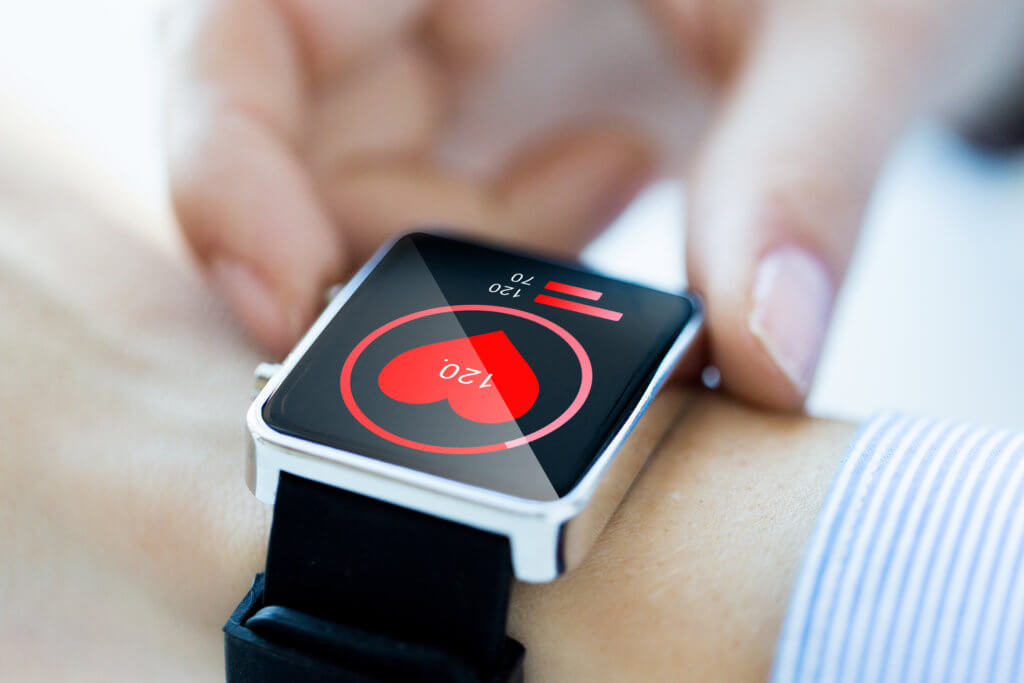
Health informatics is a type of medical application that uses data to assess the progress of health conditions, guide treatment plans, and create a more holistic picture of public health. IoT is helping health informatics harvest data and analyze it to create more insights into diagnostic medicine. For example, by combining wearables that collect data about the patient’s vitals and symptoms with hospital test results and AI, we can speed up analysis and allow algorithms to pinpoint the most likely diagnoses.
AI has been an indispensable technology for healthcare recently; in 2019, The Lancet reported that the accuracy of AI analyzing medical images was equal to the accuracy of human medical specialists. This study also caveated that relying on deep learning and machines to diagnose patients is dangerous and challenging, but by partnering with health informatics experts, the technology really shines. Without human data, experience, and perspective, a machine’s insights fall flat.
Self Management
Health informatics helps us take care of ourselves by continuing treatment, changing our lifestyle habits, and teaching us new things we could be doing to improve our health and wellness. Health informaticians have deep knowledge and insight into patient data, and they can tell us what motivates and supports us and how we can educate ourselves about our illnesses.
With the addition of IoT-enabled wearable technology, health informaticians can see real-time data on a patient’s physical condition. With platforms like New York City-based Quio, patients can connect therapeutic, IoT-enabled devices to their smartphone or computer. With their data in hand, the patient can share data about their vitals, medications, and activities with their medical provider. Using this data, the physician can develop a holistic picture of the patient between office visits. Psychologically, having control of the data also empowers the patient to take control of their health and treatments.
IoT is also adding in a much-needed element of user-friendliness to MedTech applications. If technology is too difficult to understand quickly or learn on the fly, it can scare away large groups of patients. By combining health tech with smartphone apps that are easy-to-use, patients are more motivated and encouraged to improve their wellbeing. It also improves the quality of feedback that patients leave, helping health informaticians improve their software and field for everyone.
Patient Records
Health informatics is crucial for maintaining and analyzing patient electronic medical records (EMRs). By having a patient’s full medical history including test results and scan images, medical providers can make an accurate decision in diagnosing and recommending treatments. In the past, paper records meant patients had to request their chart and wait for the provider’s office to organize all of it. Sometimes, patients faced red tape that caused further delays in diagnosis and starting treatment.

With IoT, however, EMRs are easy to collect, share, and organize, no matter how many different offices are adding patient data to a single record or which EMR application different offices are using. Even medical images, like digital x-rays, are automatically attached to the patient’s record. EMRs are available to be viewed, downloaded, and shared on portable, secured medical IoT devices like tablets and data analysis dashboards. Emergency rooms are able to start treatment in record time due to EMRs. Patients can easily access their EMRs before visiting a new doctor. These major improvements brought about by IoT are directly streamlining health informatics.
Future Outlook
Data is a critical part of technology today, and it’s become invaluable not only for the medical and healthcare fields but for patients too. Health informatics can generate actionable insights into ongoing patient wellness, diagnoses, and treatment plans and management.
With IoT, we can develop tools that support health informatics in analyzing, monitoring, and utilizing patient data. Thanks to these enhancements, patients are going to be more in control of their medical data, personal health, and wellbeing. Have you experienced IoT in medicine or health informatics? As always, let us know your thoughts or experiences in the comments below!
Tags: app developers NYC, health app, health app developer, health app development, IoT app developer New York City, iot app development, IoT app development NYC, medical app, medical app developer, medical app developers, medical app development, medical apps, mobile app development New York City, New York City app developer, New York City IoT developers, New York City mobile app development, new york IoT app developers, NYC medical app developers, tech in NYC